User Documentation#
As ipyaladin brings the Aladin Lite software into python notebooks, some commands
are similar to the original software. When this is the case, this documentation might redirect
towards Aladin Lite’s own documentation.
Initialization options for the widget#
The widget is represented by a python class, ipyaladin.widget.Aladin. This
class has arguments that allow to chose which buttons or functionalities will be
available in the widget. These cannot be edited later.
Here is a list of options that can be given to ipyaladin:
Argument |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
background_color |
rgb(60, 60, 60) |
The color behind the surveys in RGB format. |
full_screen |
False |
Whether to start in full-screen mode. |
grid_color |
rgb(178, 50, 178) |
Color of the grid. Can be specified as a named color (see html named colors), as rgb (ex: ‘rgb(178, 50, 178)’), or as a hex color (ex: ‘#86D6AE’). |
grid_opacity |
0.5 |
Opacity of the grid and labels. It is comprised between 0 and 1. |
grid_options |
{} |
More options for the grid. |
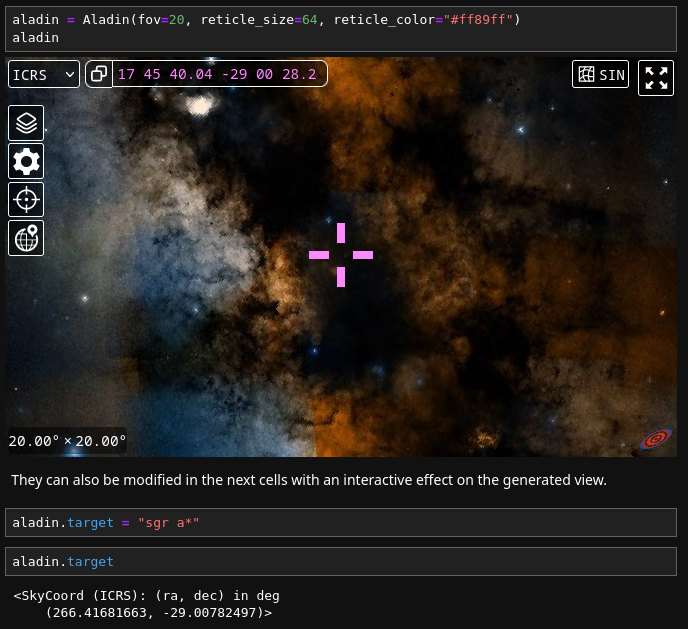
reticle_color |
rgb(178, 50, 178) |
The color of the reticle. |
reticle_size |
20 |
Whether to show the reticle in the middle. |
samp |
False |
Wether to allow sending data via the SAMP protocol. |
show_catalog |
True |
Whether to show the catalog. |
show_context_menu |
True |
Whether the right click should start the contextual menu. |
show_coo_grid |
False |
Whether the coordinates grid should be shown at startup. |
show_coo_grid_control |
True |
Whether to show the coordinate grid control toolbar. |
show_coo_location |
True |
Whether to show the coordinates bar. |
show_fov |
True |
Whether to show the field of view indicator. |
show_frame |
True |
Whether to show the viewport frame. |
show_fullscreen_control |
True |
Whether to show the fullscreen control toolbar. |
show_layers_control |
True |
Whether to show the layers control button. |
show_projection_control |
True |
Whether to show the coordinate location indicator. |
show_reticle |
True |
Whether to show the reticle in the middle of the view. |
show_settings_control |
True |
Whether to show the settings control toolbar. |
show_share_control |
False |
Whether to show the share control toolbar. |
show_simbad_pointer_control |
True |
Whether to show the Simbad pointer control toolbar. |
show_status_bar |
True |
Whether to show the status bar. |
show_zoom_control |
False |
Whether to show the zoom control toolbar. |
Setting the view’s parameters#
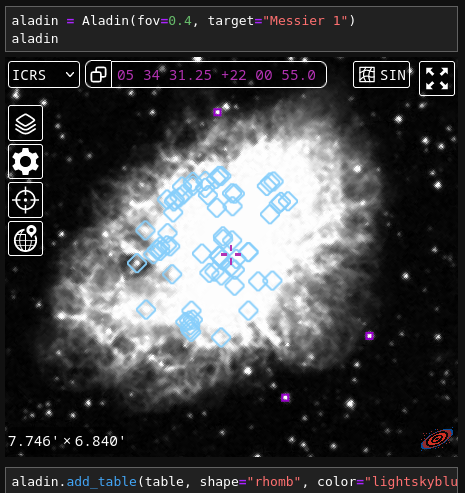
Adding elements to the widget#
Retrieving information from the current widget view#
Note about the WCS#
To calculate the WCS, ipyaladin needs to know its ows size. However, to optimize the
speed of the rendering of notebooks, Jupyter reduces the size of the output of the cells
that are outside of the view. This causes ipyaladin to calculate WCS with the wrong
field of view. We raise a WidgetReducedError in this case. Here are a few
workarounds for this issue:
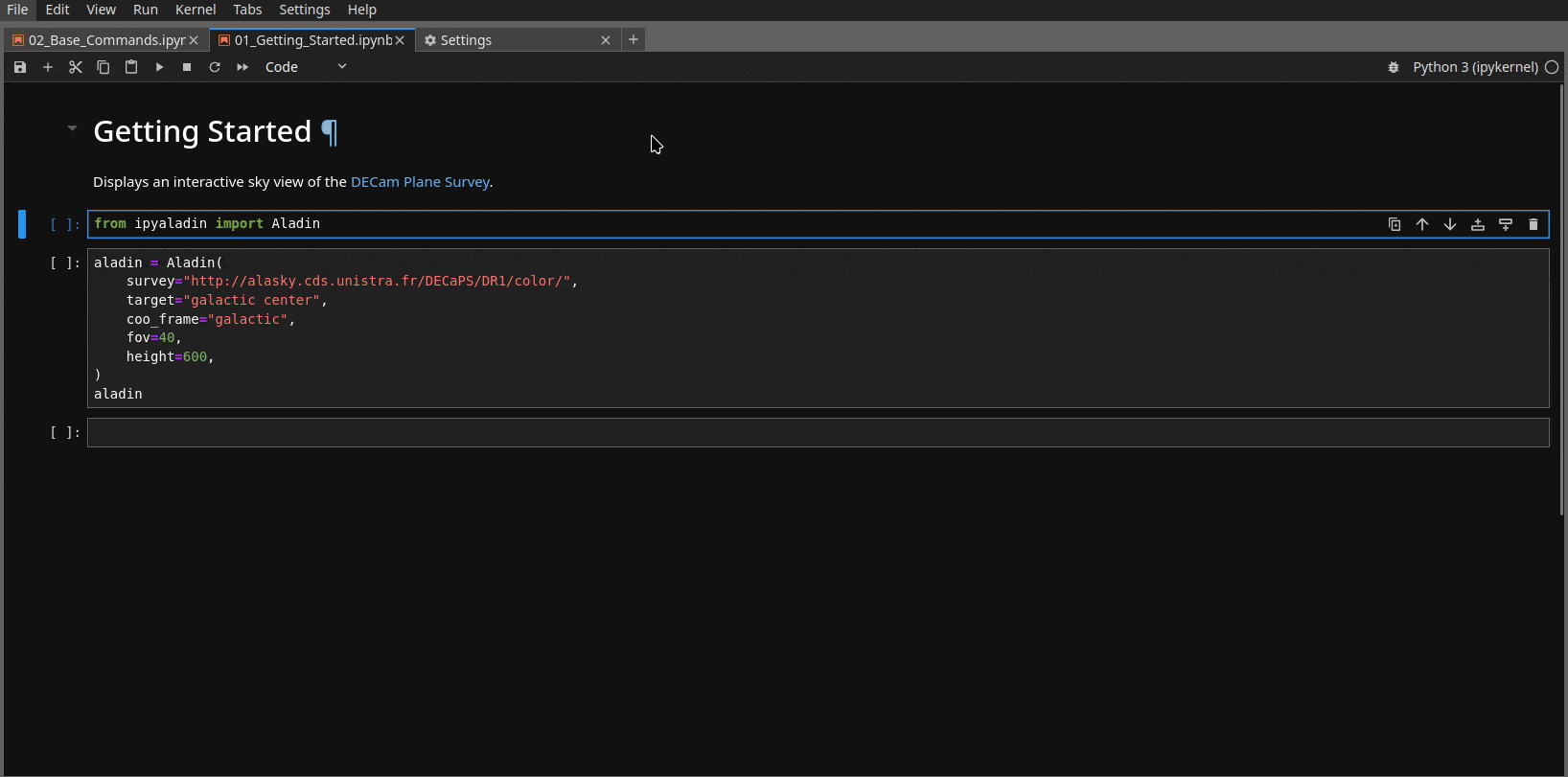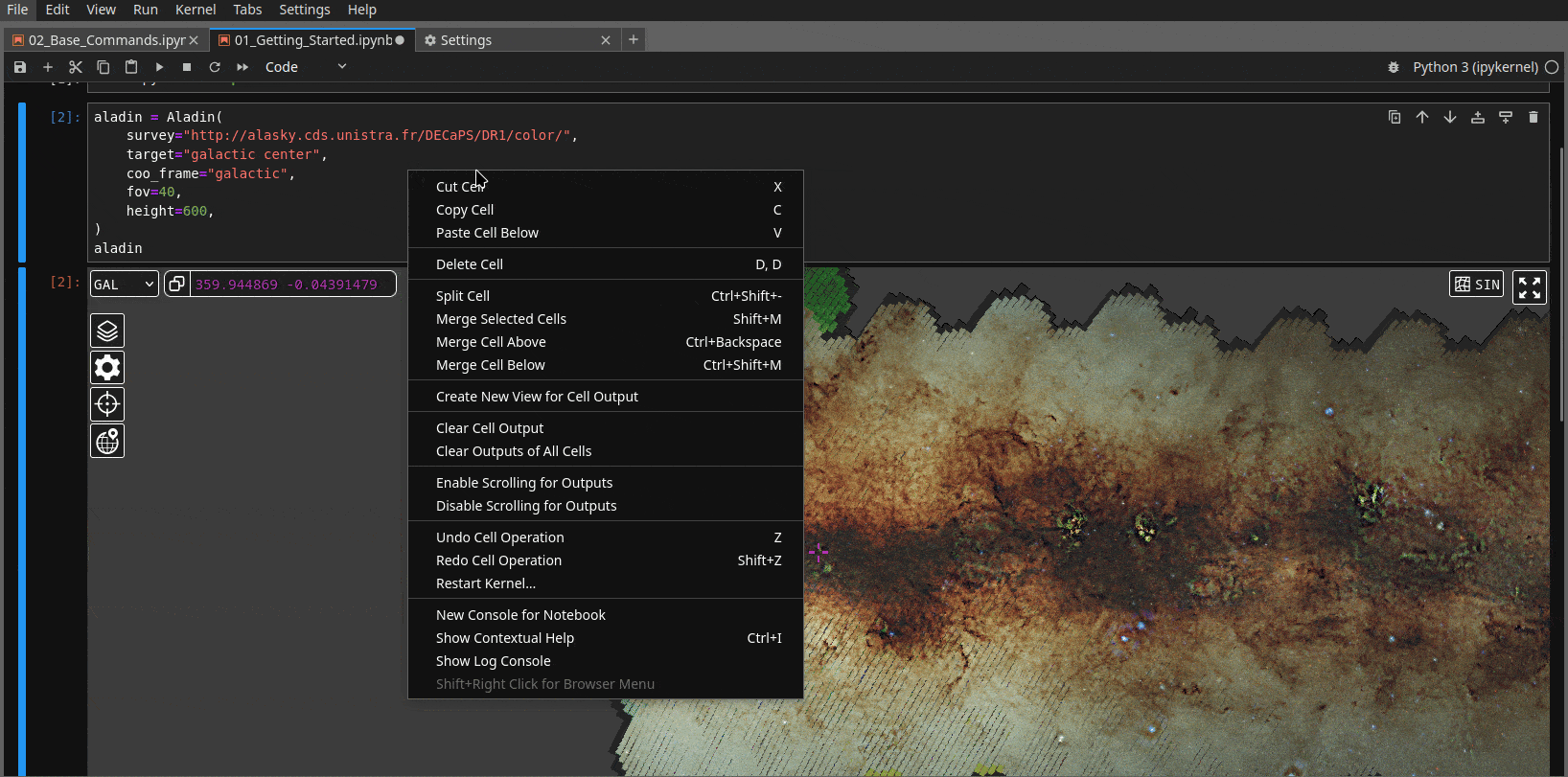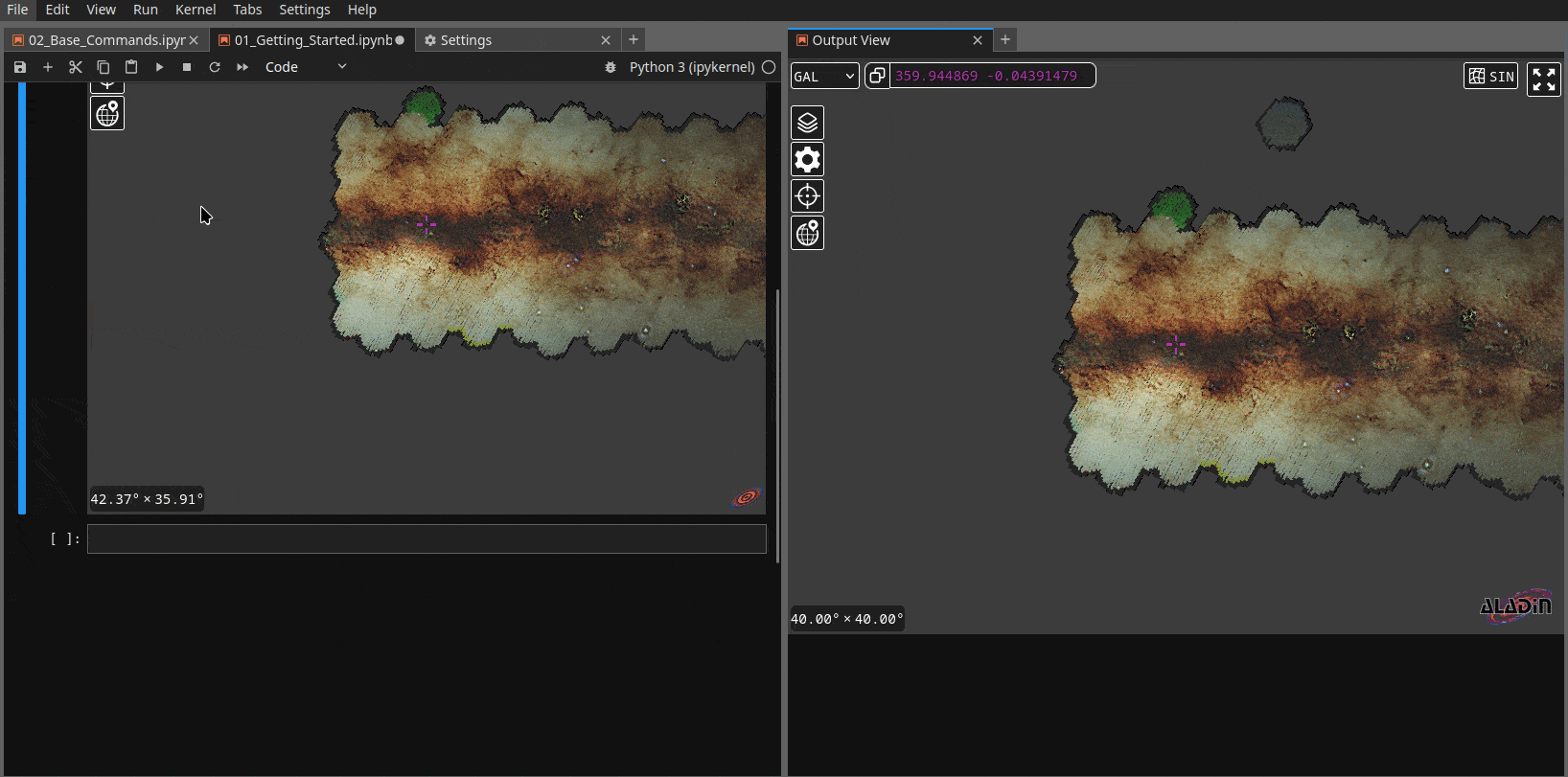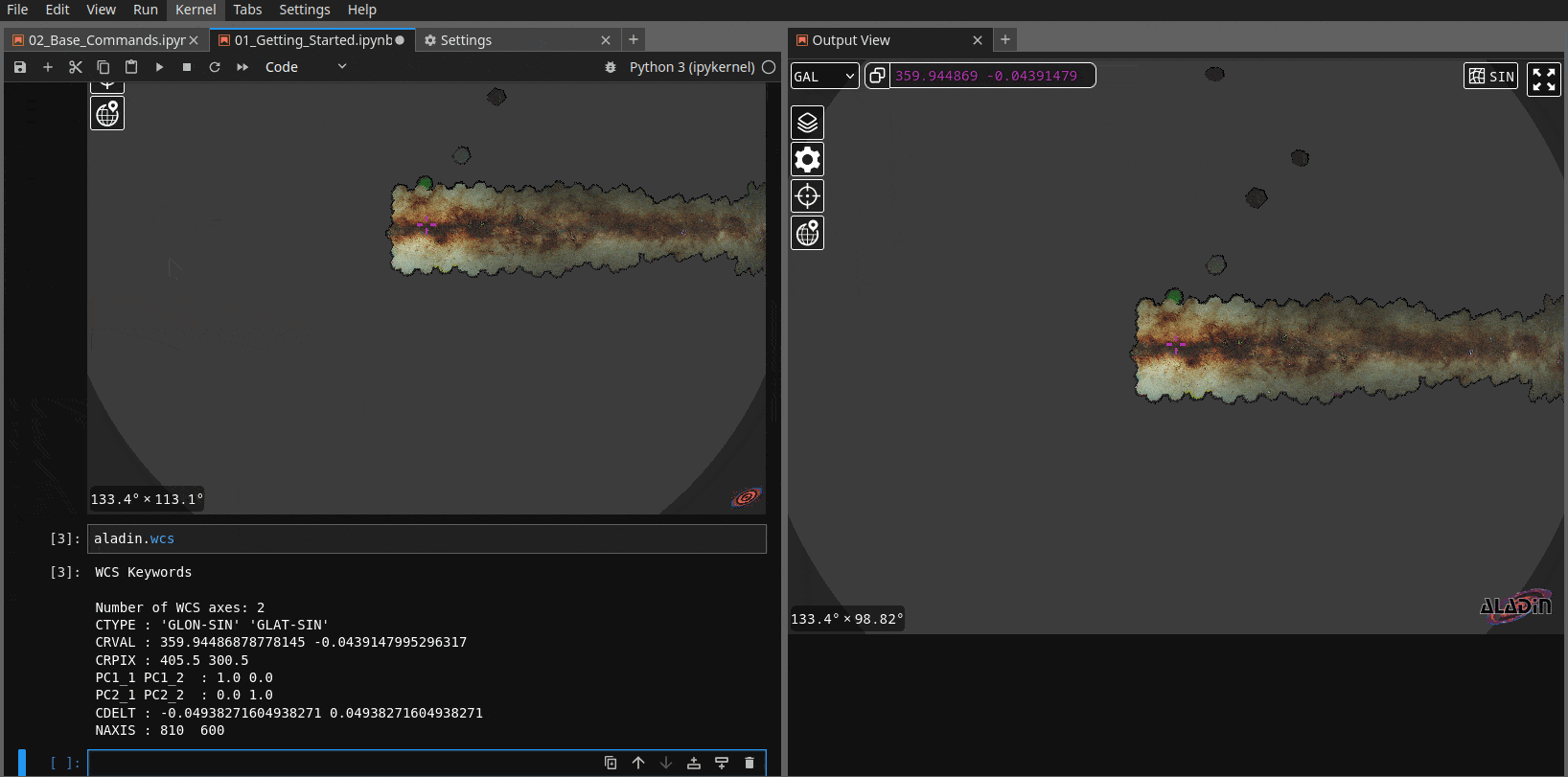
1. Detaching the widget from the notebook and keeping it on the side of the notebook#
In Jupyter notebook, you can right click on the cell where ipyaladin is displayed,
then chose Create new view for cell output in the menu. This way, it is never out of
the view (we also find it very practical) and the returned WCS will correspond to the
view on the side.
2. Disabling the optimization in the notebook parameters#
To disable the option that reduces the widget when it is out of the view, you can go to
Settings, Settings Editor, Notebook, and set Windowing mode to none.
This can make your notebook slower if you have a lot of cells.
Advanced use#
ipyaladin can be combined with widgets from the ipywidgets library to create
interactive cell outputs.