Journey of your data in the VO and EOSC
Last updated on 2023-09-07 | Edit this page
Overview
Questions
- What happens to your data after their ingestion in VizieR?
- Why publish to EOSC / VO?
- How do you find your data in EOSC?
Objectives
- Describe the integration of astronomy data services in the VO and EOSC
- Naviguate through the EOSC portal
From VizieR to EOSC
In the previous chapters, we concentrated on the publication of data via the CDS VizieR service. We will now show how the process leads to the data being made visible in the EOSC Portal. We invite astronomy researchers to follow the journey of their data to EOSC!
Once your data have been successfully ingested into VizieR, they begin their journey into the Virtual Observatory, as illustrated in the figure below.

Work within the ESCAPE project and the EOSC Future project has been aimed at connecting the existing astronomy data publishing systems to the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC).
The first stop for your data after VizieR is the International Virtual Observatory Alliance (IVOA) registry. It gathers the data from ViZieR, and other astronomical data centers.
Then the datasets reach a broader audience when EUDAT/B2Find and the EOSC registries gather information (harvest) about everything emitted by the IVOA registry. In this way the familiar processes of publishing data become part of the wider EOSC system.
The European Open Science Cloud (EOSC)
EOSC is the European web of FAIR data and related services for research. It stands for European Open Science Cloud and it aims to make research data easy to find, access, interoperate and reuse (FAIR), making trusted and sustainable research outputs available within and across scientific disciplines.
The EOSC ambition is to federate existing data, research and e-infrastructures to make them all available to European researchers across borders and across disciplines.
EOSC Portal
The EOSC Portal is one of the results of the EOSC Future, European Commission funded project (2019-2023). It provides an interface to EOSC for researchers to utilise the full spectrum of EOSC resources, which include research publications, data, software, and value-added services to support their research.
For prospective users of the services, the Portal provides training materials and tutorials on how to use its features. The Portal also offers information for potential service providers on how to onboard their services to the EOSC Portal Catalogue & Marketplace.
Case Study: Gaia DR3
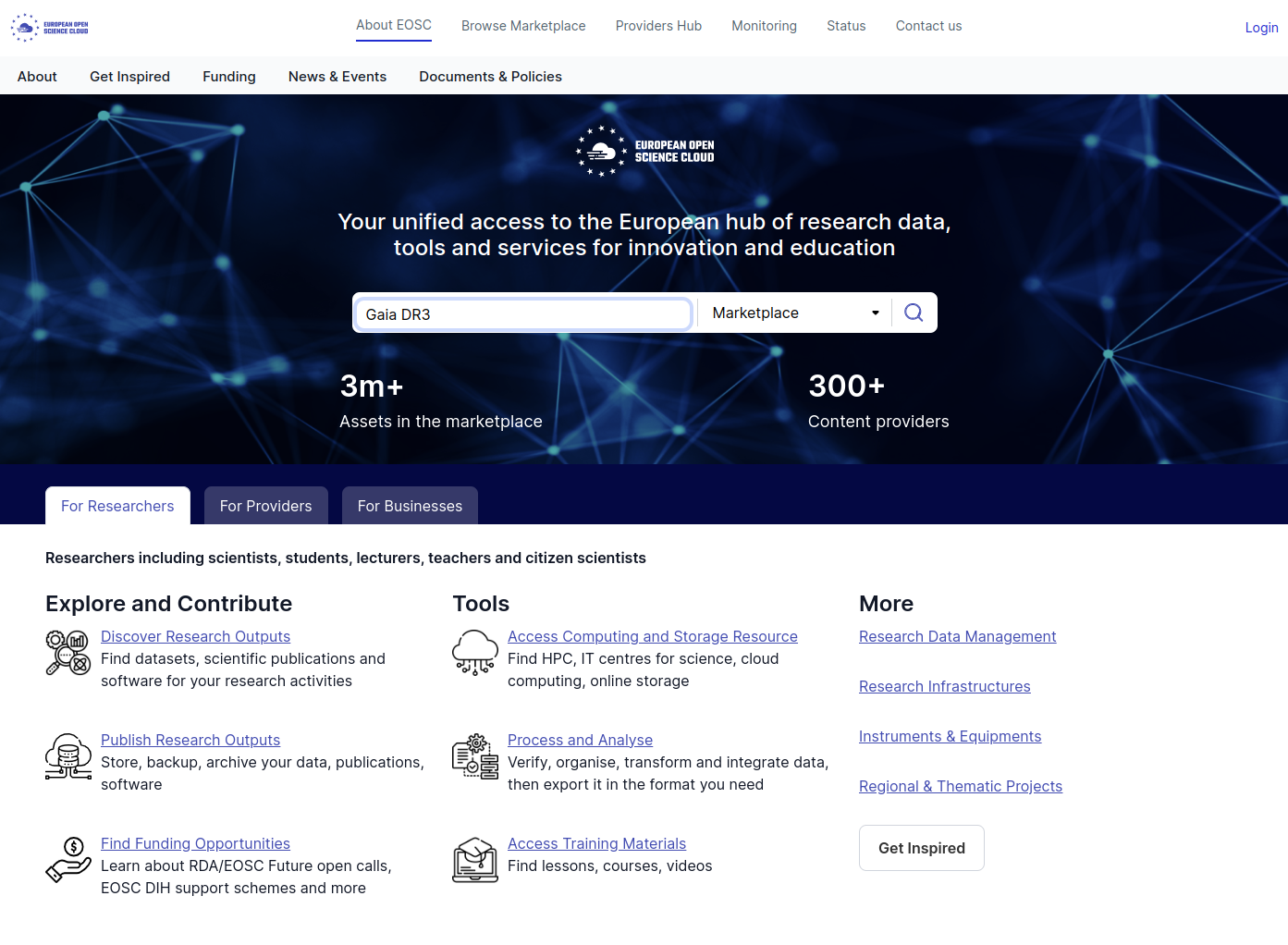
In the following, we will show how to find your data in EOSC, using Gaia DR3 (VizieR DOI: 10.26093/cds/vizier.1355) as an example.
Step 1: Search
The first step is to type the name of your catalogue, dataset, paper, DOI in the Search bar on EOSC portal, as illustrated in the figure below.
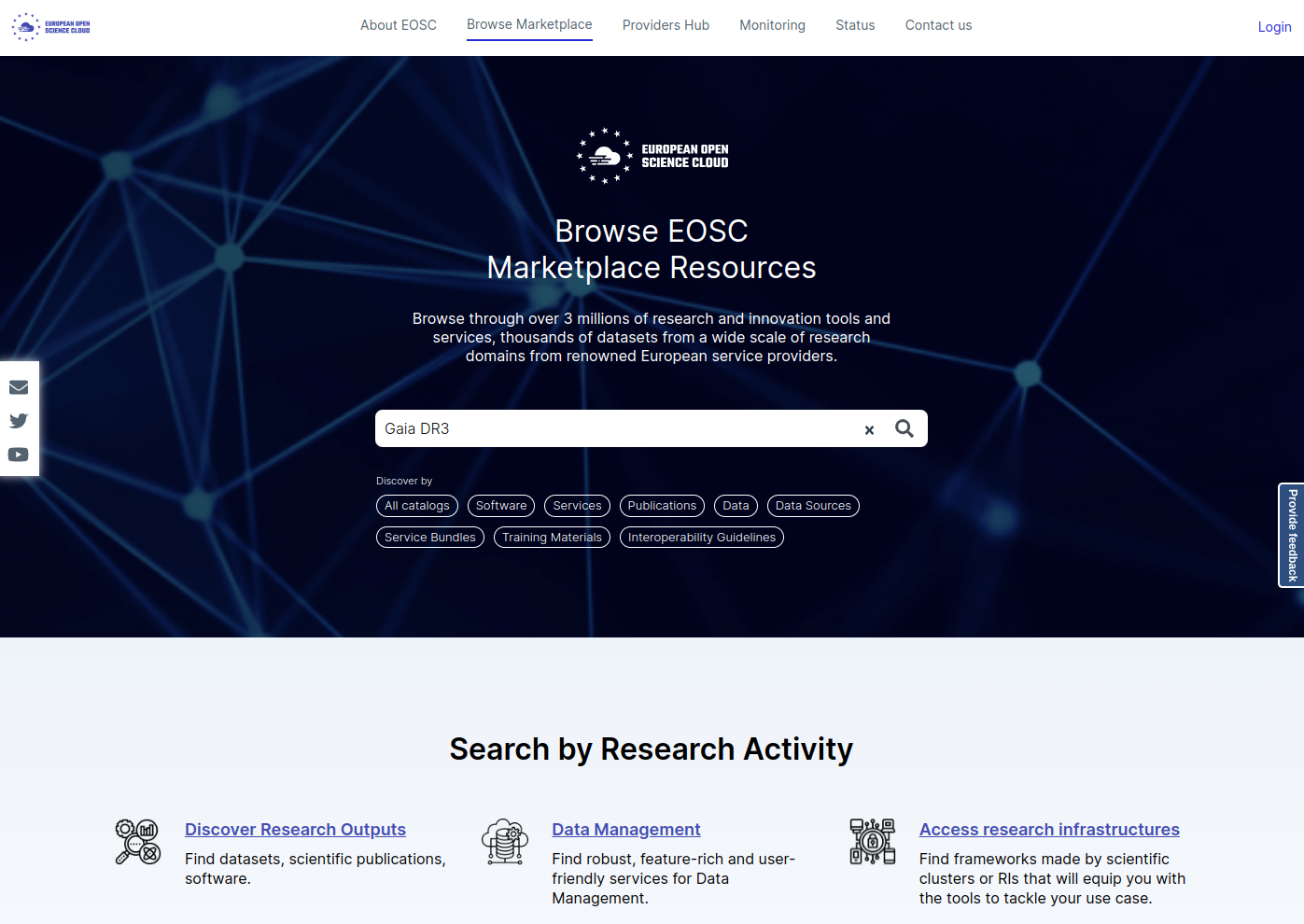
You can also browse directly the Marketplace, from the same website. You will get the same results in the end.
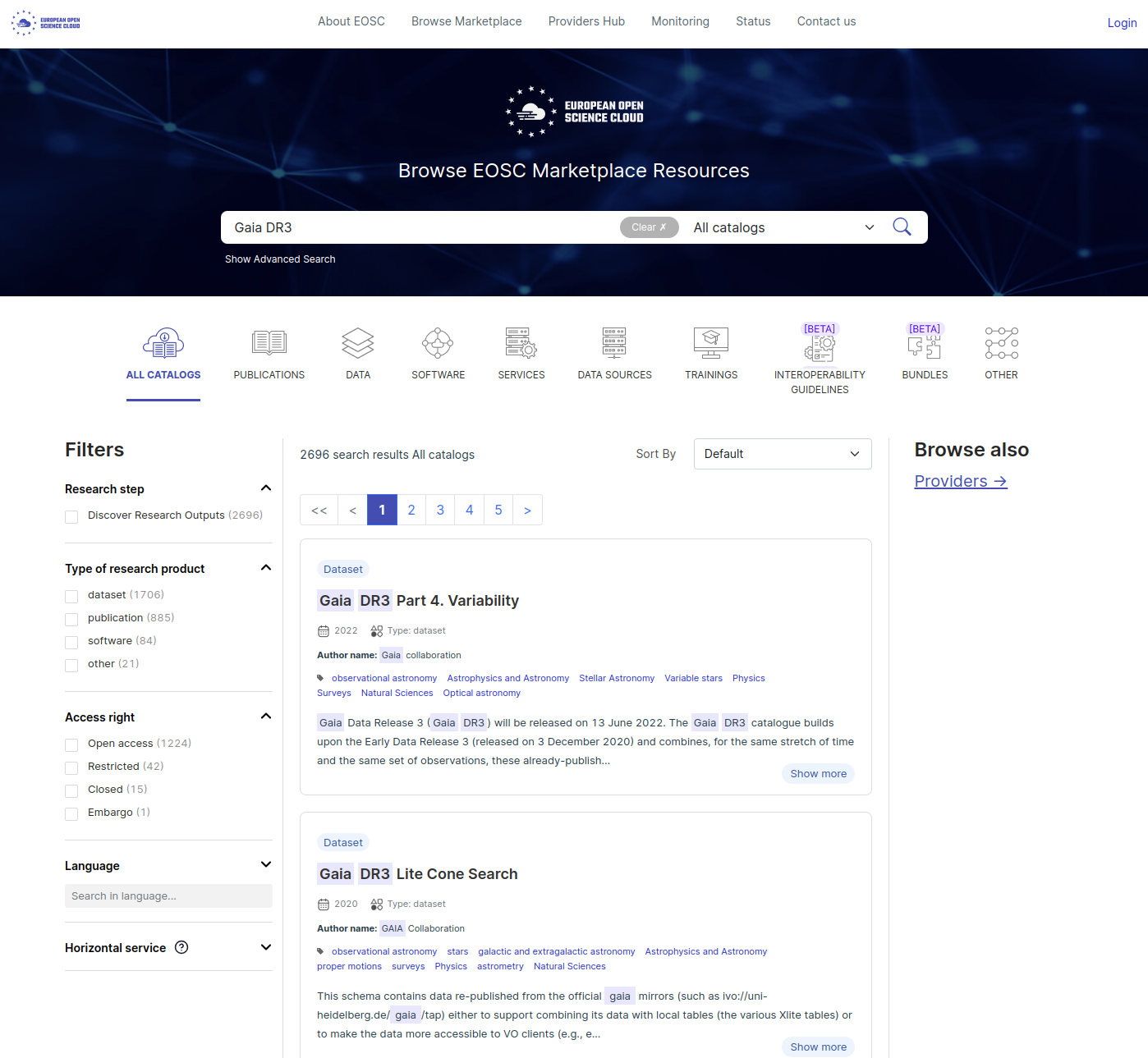
Step 2: Scan list of records
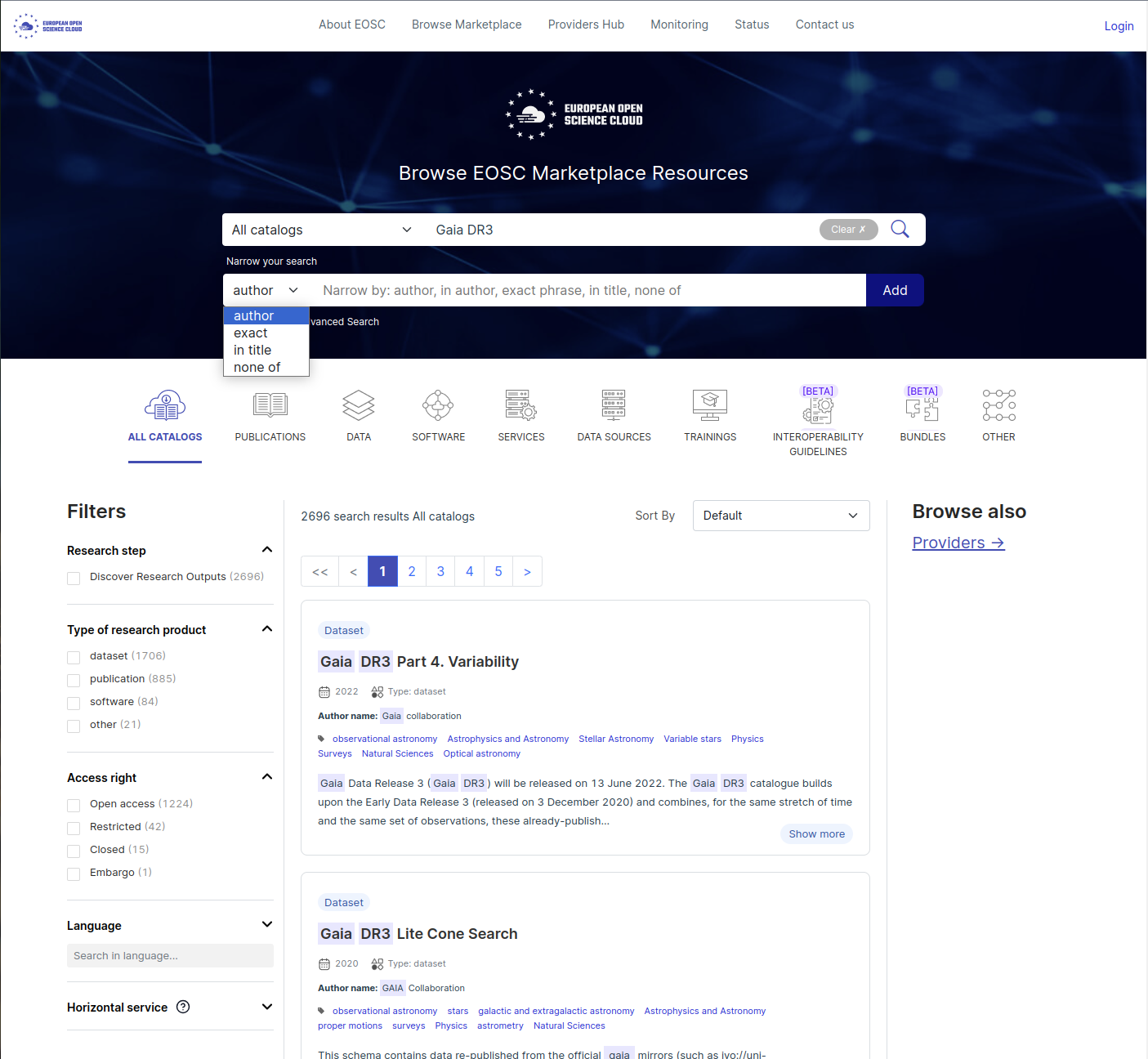
A full list of search results appear (link to all results), as illustrated in the figure below. You can filter the results using the ‘Filters’ options on the left, or also by type of data at the top (eg. Catalogs, Publications, Data, Software …).
In our example (Gaia DR3), we can see that the search is done on multiple fields: Title, Author names, abstract.
Advanced search
In addition to the filters available on the left side of the EOSC Marketplace results page, more advanced filtering can be done using the ‘Show Advanced Search’ button below the main Search bar.
The search can be narrowed by ‘author’, ‘exact phrase’, ‘in title’, ‘none of’, as illustrated in the Figure below.
Step 3: Select an entry
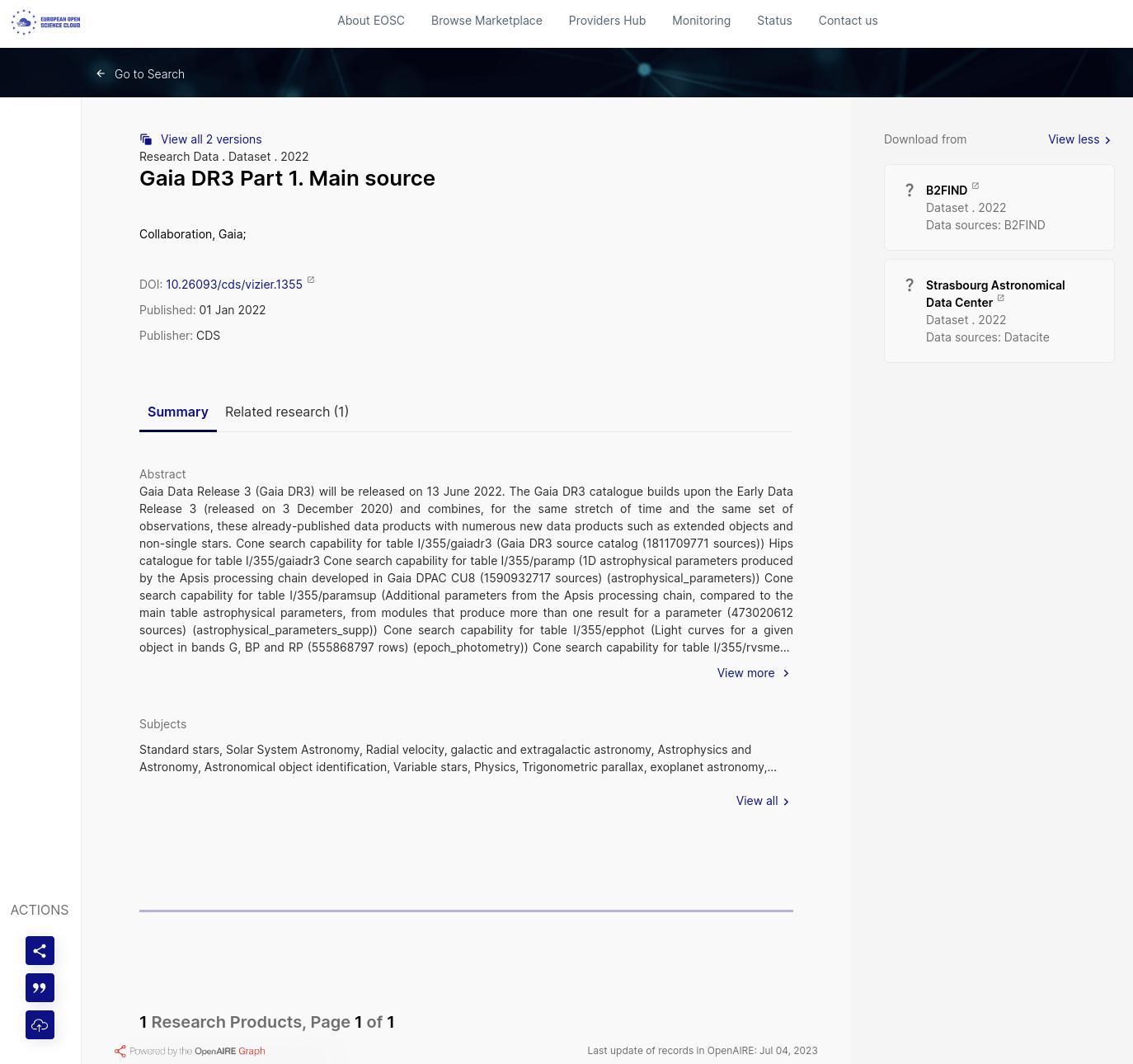
Once you found the relevant entry, you can click on it (link to selected result) and see many informations: Title, DOI, Date of publication, Publisher, Abstract, Relevant subjects (keywords), as illustrated in the figure below.
In this example, you can access to the resource by either clicking on the DOI link, or on the ‘Download from’ on the right side of the EOSC page, and then select one of the two data sources available: B2FIND or Strasbourg Astronomical Data Center.
Examples: try it yourself
Can you answer the following questions?
Q1) What is the publication date for ‘Brightest cluster galaxies in Abell clusters’?
Q2) Which CDS service is listed in the ‘Services’ type of results?
Q3) Can you list some ‘cds-astro’ Softwares available?
Q4) Advanced question: can you find the dataset associated with the ‘National Radio Astronomy Observatory’?
Q5) If you published a paper or a dataset, type your name in the Search bar. What do you get as an output?
Browse through EOSC Portal to answer the previous questions.
R1) This paper was published on 01 Jan 2017.
R2) SIMBAD is the service accessible through EOSC portal.
R3) Examples of softwares available: cds-astro/tutorials: v1.0.0, cds-astro/aladin-lite: Aladin Lite v3.1.1, cds-astro/cds-moc-rust: Release v0.5.2, cds-astro/mocpy: Release v0.12.3 …
R4) Leave the Search bar empty, and type ‘National Radio Astronomy Observatory’ as the author in Advanced Search. Launch the search by clicking on the ‘Add’ button.
The search result Data should look like: search-result.
Summary
EOSC is not a new digital infrastructure.
EOSC will support the cultural change towards Open Science and FAIR principles in the European countries and institutions.
Individual researchers will benefits from EOSC through their existing channels (e.g. universities, research institutes, research infrastructures, associations, science clusters, etc.) that will act as intermediaries.
EOSC will allow for universal access to data and a new level playing field for European researchers.
-
EOSC Portal Catalogue & Marketplace acts as an entry point to a multitude of services and resources for researchers, such as:
- Discover Research Outputs (datasets, scientific publications, softwares)
- Access Training Materials (lessons, courses, videos)
The catalogues ingested in VizieR are findable and accessible in EOSC!
Interdisciplinary science is facilitated using EOSC Portal, thanks to the interoperability of the data.
EOSC promotes the reuse of the data.
End!
This concludes this training on how to make your published astronomical data (table, images, spectra, …) FAIR and openly accessible to the community, and discoverable in Virtual Observatory tools such as EOSC.
